Update 1st August 2013
The DIA have now confirmed that they did filter some sites hosted by Google and that this caused problems for both the filter and some internet users.
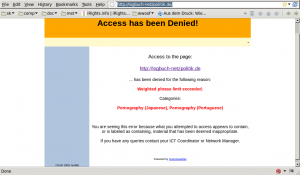
Officials provided an oral briefing on the incident reported regarding a degradation of service noted by some users of certain services. The Filter Operations Team worked with the provider of those services in question. It was discovered that hentai and cgi based child abuse sites hosted on the blogspot.com domain, a resource operated by Google Inc were included in the list in error.These sites were then shown to the IRG. It was then explained that a list refresh, removed the sites in question, and subsequently resolved this issue.
The problem was further compounded by the severe congestion in the networks of one of the upstream providers used by the system. A review of the Filter’s failsafe systems was undertaken. Steps have been added to ensure that the IPs of large hosting providers are flagged and placed on a white list with a reporting mechanism for the removal of the content from the site. Additional resources were requested from the upstream provider in question to ensure traffic congestion can be avoided in the future.
Back in 2011 we spotted the first indications of how the Department of Internal Affairs Internet filter, used by 90% of all New Zealand Internet connections, actually operates. At the time, we noticed an address – 124.150.165.62 – appearing where it shouldn’t in traceroutes to a site.
Performance Problems
Now that same address has popped up in traces to Google addresses, specifically googlehosted.l.googleusercontent.com (74.125.237.11). As noted in this thread on Geekzone, some people have been experiencing performance problems reaching some Google services.
These performance problems could be caused by a Google-load of traffic to that IP being routed to the DIA’s filtering server which may not be coping with the volume. Note that the filter will only be blocking one web address (URL) at that IP and letting the rest of the traffic through.
Of course this won’t affect you if you are using an ISP that doesn’t use the filter. Check the list of ISPs here.
Making the link
As noted back in 2011, the address appearing in traces where they shouldn’t be are controlled by Fastcom, who list the Department of Internet Affairs as an important customer and which they host infrastructure for.
Filtering problems
This was always one of the fears when the filter was introduced – that it would reduce the stability and performance of the New Zealand internet. It appears that this has now happened. Two questions:
- Will the DIA remove the entry for this IP now that they realise the problems it’s causing?
- How will the DIA block web addresses hosted at high volume websites such as Google (or Wikipedia) when the filter can’t cope?
Seeking more information
Have you been experiencing any issues accessing Google? Can you provide a traceroute for us? Post a comment below.
Rumours and hearsay
Thanks to the people who contacted us with more information, we just wish you were prepared to speak on the record. So far we have heard the following from people that we typically find to be reliable:
- That the DIA has denied filtering that IP address.
- That a senior ISP engineer says that the IP address was definitely filtered by the DIA filter and that they have seen the relevant BGP records.
- That the filtering of at least one Google IP address has been removed but that there might be more.
- That Google was greatly annoyed by the block and contacted the Minister to get it removed.
We’ll update these rumours as we can confirm/deny them. Please email any information to thomas@techliberty.org.nz. We will do our best to keep your name confidential if requested, but suggest using an anonymous remailer for the best anonymity.